Different Types of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for Men
There are multiple different types of testosterone replacement therapy. Once diagnosed with testosterone deficiency (low testosterone), it can be a bit overwhelming to work out which form of testosterone to start on. Here I outline the different forms of testosterone, and some of the benefits and negatives of each. This decision should always be made in collaboration with a physician & tailored to you.
If you are struggling with symptoms of low testosterone, or you’ve been on TRT but have stopped seeing benefits, do book an appointment with me to discuss further. I help many men work out whether testosterone is really the issue, and what the right treatment is for them. You can find out more about me here.
Gels or Injections?
The first decision is topical testosterone (a cream or gel you apply to the skin), versus injectable testosterone. Many men have negative views about gels, but for many men they work well, have fewer side effects and mean they don’t have to deal with needles.
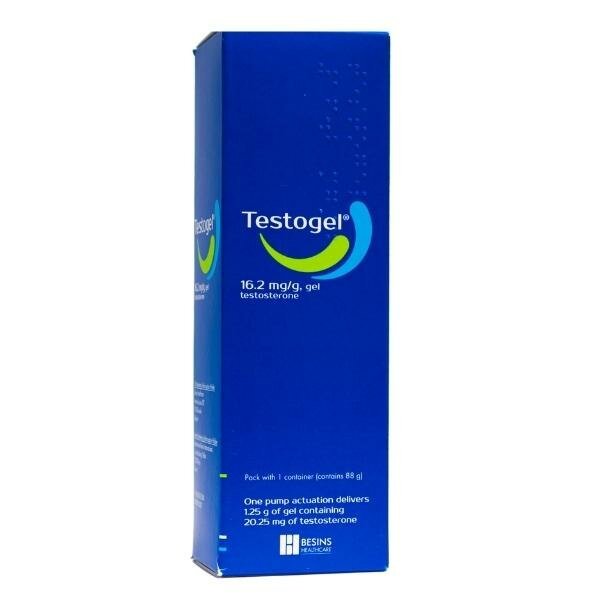
Topical Testosterone - Creams and Gels
Advantages
Topical testosterone is easy to use.
It doesn’t involve any injections or needles.
Lower risk of side effects: hardly ever causes raised oestrogen, haematocrit or acne vs injectables
We have really good long term data on the cardiovascular safety of topical testosterone (TRAVERSE study)
Disadvantages:
Daily application
Need to wait for it to dry for a few minutes
Some men don’t absorb it so well
Risk of transfer to another person
Cost:
Depends on dose.
For a standard dose: Approx £45/month
Injectable Forms of Testosterone
There are several different forms of injectable testosterone, the most common are:
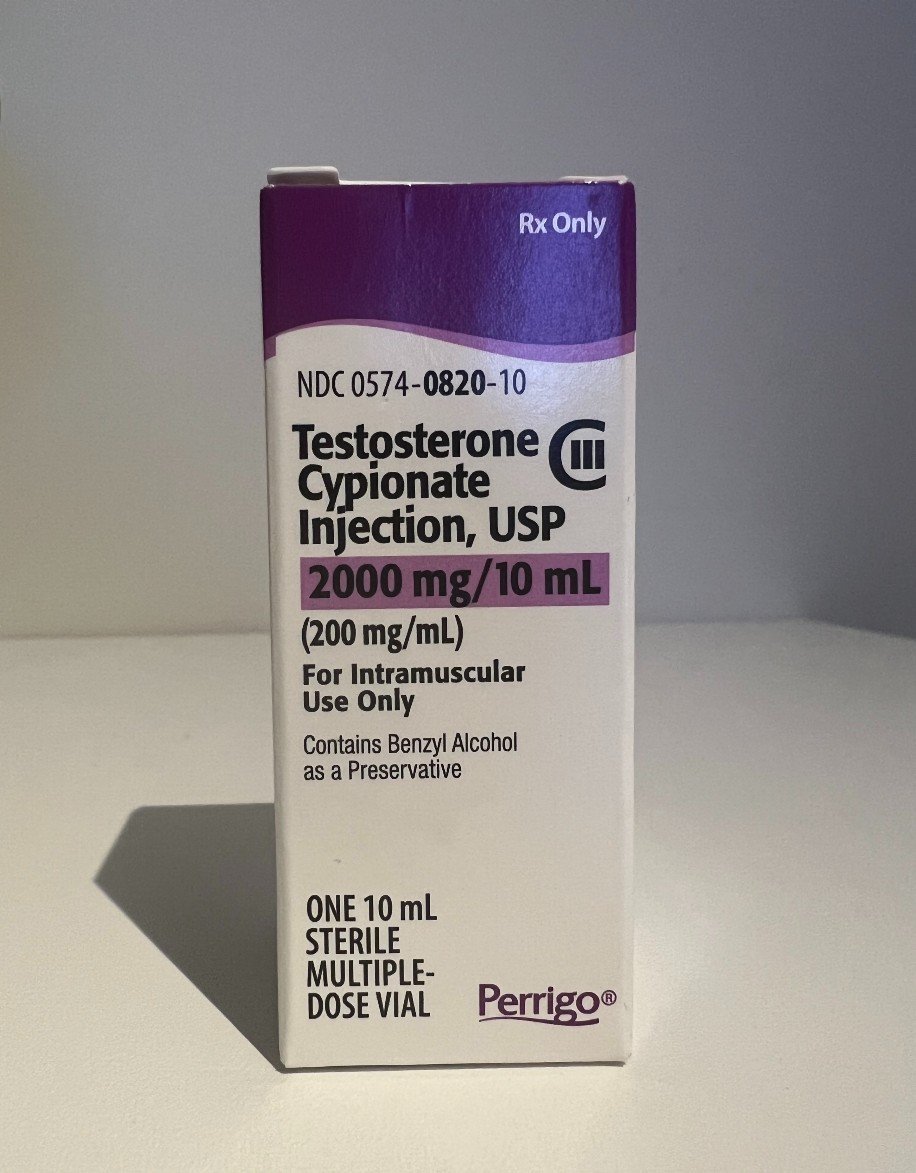
Testosterone Cypionate
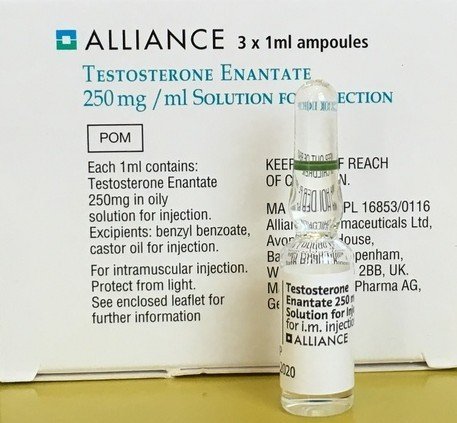
Testosterone Enanthate
Sustanon
Testosterone Undecanoate (Nebido)
For Cypionate, Enanthate and Sustanon, injectable equipment is needed, which costs approximately £40-50 for 3 months’ supply
Testosterone Cypionate
Advantages
Single testosterone ester, not a mix of testosterones, means it has a predictable effect over time with a stable level of testosterone achieved easily
Can be used to inject into fat rather than muscle
Can be used for more frequent injection (three times a week), which has some advantages
Olive oil carrier oil, which causes less reaction than other oil bases
Disadvantages
Imported from the USA and so more costly.
For some, frequent injection is a pain
Not licensed in the UK, but used off license
Cost:
Approximately £215 for 4 months’ supply, plus cost of injecting equipment
Testosterone Enanthate
Advantages
Single ester which might enable more predictable stable levels
Can be used for microdosing (e.g. twice weekly injections)
Disadvantages
Only suitable for intramuscular injection, not so suitable for injection into the fat
Carrier oil is castor oil, which can cause some men more reactions / pain
Cost
Cost very variable up to £60/month plus costs of injecting equipment
Sustanon
Sustanon is a mix of four different types of testosterone. Each has a different half life. This was designed to reduce the ups and downs of testosterone levels, which works for some men.
Its licensed for injection every three weeks, but many men find that they feel pretty awful in the third week when their levels drop. Instead it can be microdosed, injecting a small amount once or twice a week.
Advantages:
Cheap - £10/month
Can be used for microdosing
Licensed in the UK & readily available
Disadvantages
Some men don’t do well with the multiple esters, although this is rare
It can’t be used subcutaneously
Often not available outside Europe & the UK
Nebido
Advantages:
Licensed in the UK
Slow release testosterone. Only one injection needed every 3 months after first 3 months - therefore fewer injections
Disadvantages:
Levels change over the course of the three months, which some find unsatisfactory
Large volume of injection
More difficult to adjust levels. Once the medication is in, it is there for three months
Cost:
Cost is approximately £100/3 months
There are multiple different options for testosterone replacement and discussing each with your doctor is important to work out what is right for you. The above is no substitute for advice from a suitably qualified doctor.
It can take time to work out the right solution for you. Some men start on one form and then switch to another form after some time, if this isn’t working for them. There is no once size fits all.
I specialise in men who have been on TRT but still have symptoms, or where there is a question around whether testosterone deficiency is the right diagnosis. Many men struggle with sexual symptoms which end up being treated with testosterone, even when testosterone deficiency isn’t really the issue. As a clinical sexologist I look at the whole picture - medical and psychosexual - to find a way forward for men with symptoms of low sexual desire, erectile difficulties and low mood - whether the issue is medical or more psychological.
Thinking about starting to take testosterone?
Being prescribed or recommended testosterone from an online clinic?